Course 8 - Penetration Testing OSINT Gathering with Recon-ng | Episode 2: Modules, Data Flow, Naming Structure, API Keys
Update: 2025-11-16
Description
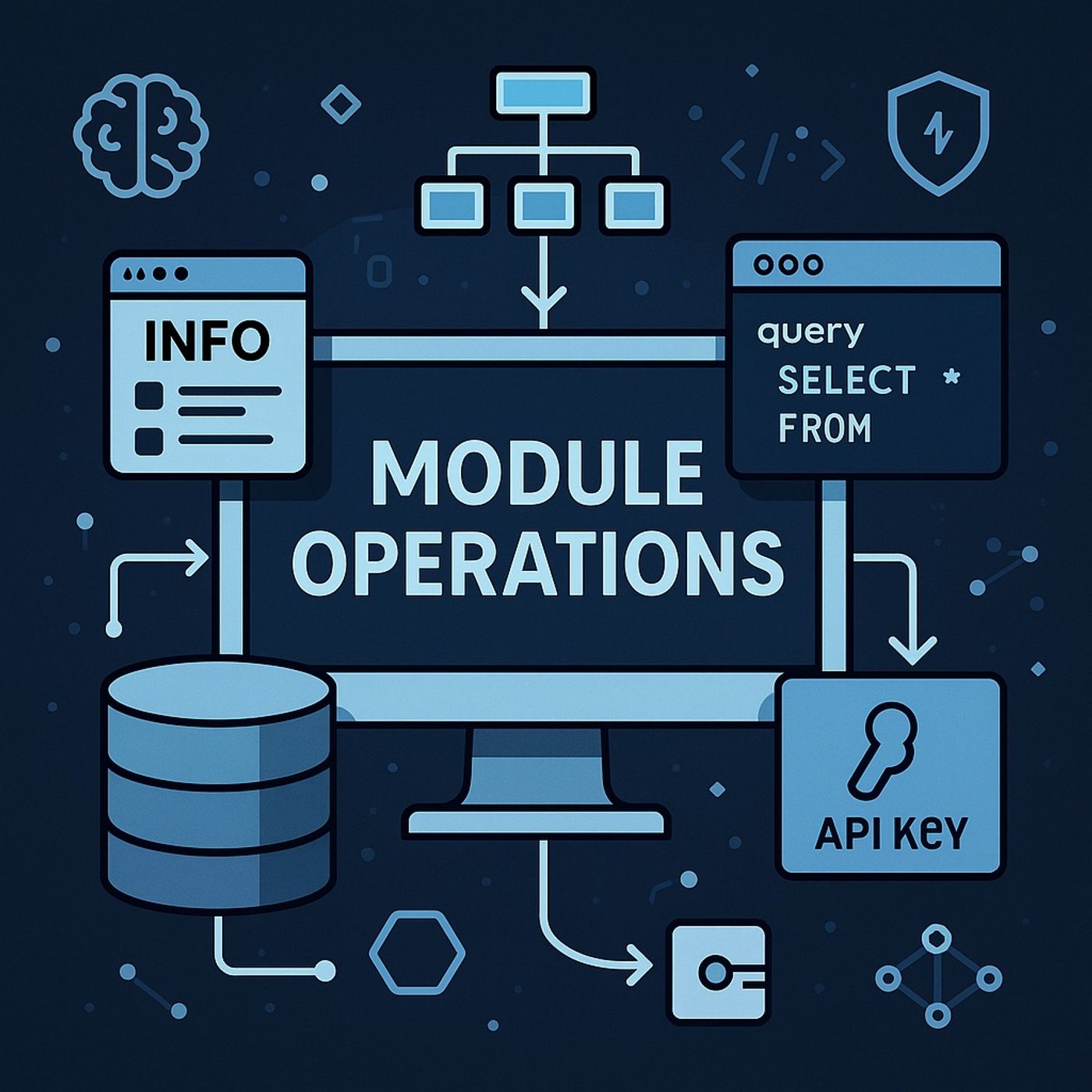
In this lesson, you’ll learn about: Mastering Recon-ng Module Operations, Data Flow, Naming Structure, API Integration & Session Automation 1. Understanding Module Functionality To operate any module correctly, analysts must inspect its requirements using:
Retrieve contacts belonging to one domain instead of dumping the entire contacts table. This improves workflow efficiency when processing large OSINT datasets. 5. Module Configuration Modules can be customized using:
You can listen and download our episodes for free on more than 10 different platforms:
https://linktr.ee/cybercode_academy
- show info — displays the module’s:
- Name
- Description
- Required and optional inputs
- Source and destination database tables
- Modules read from specific database tables (e.g., domains, hosts)
- Then write results to other tables (e.g., contacts, repositories)
- Use a domain enumeration module (e.g., google_site_web)
→ populates the hosts table - Then run a discovery module (e.g., interesting_files)
→ requires the hosts table to be populated to search for files
- query command → perform SQL-like lookups
- run + SQL syntax → filter large datasets
Retrieve contacts belonging to one domain instead of dumping the entire contacts table. This improves workflow efficiency when processing large OSINT datasets. 5. Module Configuration Modules can be customized using:
- set → assign a value (e.g., limit results, pick target subdomains)
- unset → remove the assigned value
- Reconnaissance
- Reporting
- Import
- Discovery
- Each module name reflects the source → destination flow
- Example: domains-hosts means “take domains and discover hosts”
- Common tables used include:
- companies
- contacts
- domains
- hosts
- netblocks
- profiles
- repositories
- keys add → configure an API key
- show keys → list all installed keys
- record start → begin recording commands
- record stop → stop recording
- Run recorded script using:
recon-ng -r
- spool → log everything output in the session
Useful for audits, reporting, and compliance documentation.
- Understand module requirements (show info)
- Chain modules effectively using database-driven workflows
- Customize modules with set and unset
- Use Recon-ng’s SQL-like querying for precise data extraction
- Manage API keys for enhanced OSINT data
- Automate tasks using recording and spooling
You can listen and download our episodes for free on more than 10 different platforms:
https://linktr.ee/cybercode_academy
Comments
In Channel